Your privacy is very important to us. When you visit our website, please agree to the use of all cookies. For more information about personal data processing, please go to Privacy Policy.


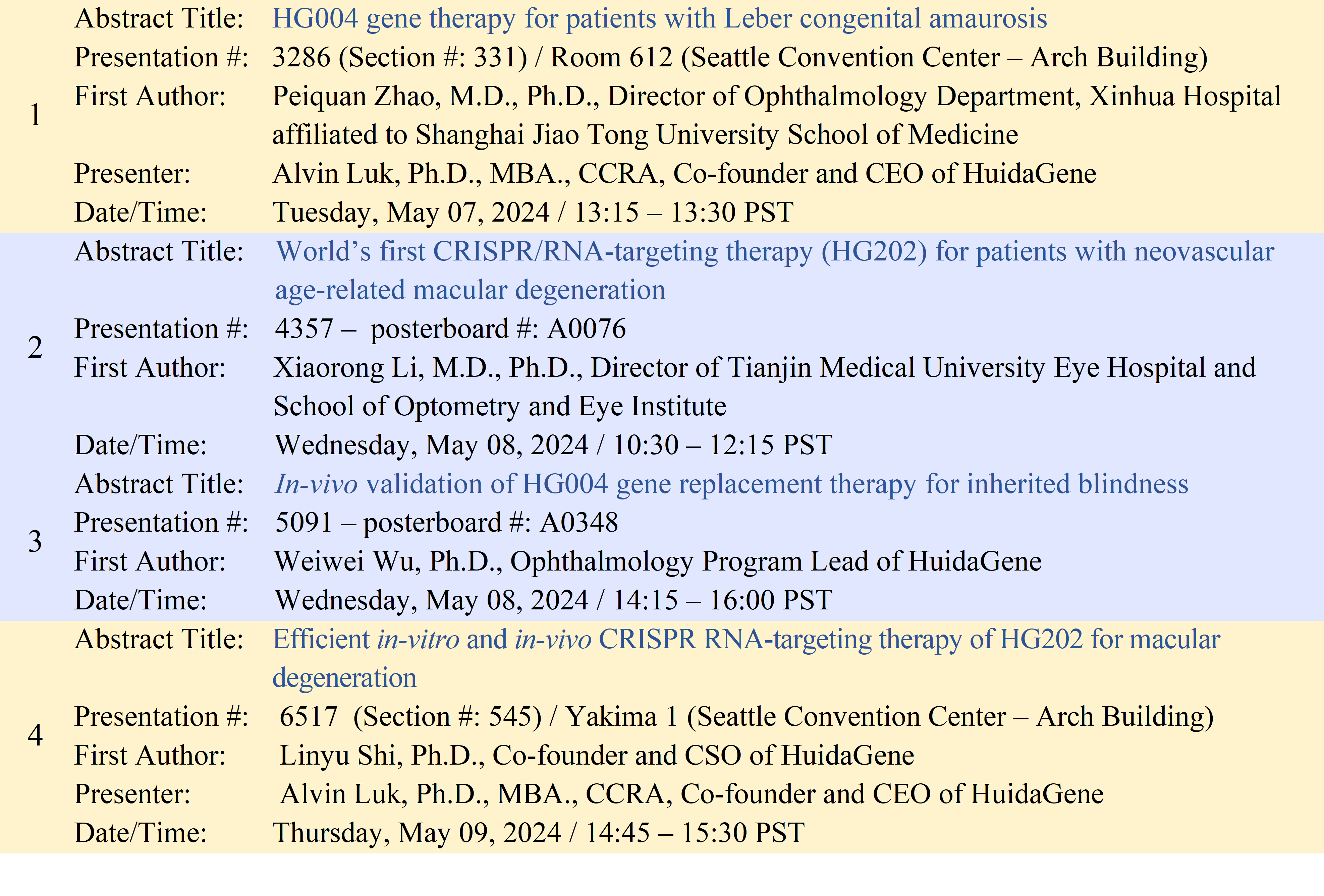
HuidaGene Orally Presents Data Highlighting Strength of Ophthalmology Portfolio at the 2024 Association for Research in Visual and Ophthalmology Annual Meeting
· Oral presentation of HG004 gene augmentation therapy restores the function of RPE-photoreceptor cells in the Rpe65-/- murine model and demonstrates significant improvement of visual and retinal functions in LCA2 patients.
· Oral presentation of HG202 CRISPR RNA-targeting therapy reduces neovascularization in mice with laser-induced CNV and potentially treats nAMD patients who are non-responsive or treatment-resistant to anti-VEGF therapies.
SHANGHAI and CLINTON (NJ), April 15, 2024 – HuidaGene Therapeutics (“HuidaGene”), a global clinical-stage biotechnology company developing potentially curative genomic medicines, today announced its participation at the Association for Research in Visual and Ophthalmology (ARVO) Annual Meeting being held May 5-9, 2024, in Seattle, Washington, where over 11,000 experts from across the globe gathering to share the latest most cutting-edge research findings and collaborate on innovative solutions for the future. These four abstracts (including 2 oral presentations) showcase the strength and potential of the Company’s Ophthalmology portfolio in gene replacement therapy and CRISPR/Cas13 RNA targeting therapy to treat a wide range of retinal diseases.
“We saw substantial restoration of vision in patients living with Leber congenital amaurosis who have no treatment options currently in China,” said Prof. Peiquan Zhao, Director of Ophthalmology Department at Xinhua Hospital affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. “After only a single, one-time administration, all of the patients given HG004 had improvement in retinal sensitivity and there were no serious adverse events, including retinal detachment, have been observed. This trial data of the ‘LIGHT’ study is the first time been discussed in an oral presentation at an international conference. As the principal investigator of the study, I am committed to working with global stakeholders to bring this safe and effective treatment to patients with LCA and bring light to patients with ophthalmic diseases worldwide.”
Further information on HuidaGene’s abstracts that will be presented at ARVO 2024 can be found in the table below.
“Long-term expression of VEGF antibody using AAV gene therapy expressing anti-VEGF antibody may excessively inhibit the function of VEGF and affect the function of angiogenesis,” said Alvin Luk, Ph.D., MBA., CCRA, Co-Founder and CEO of HuidaGene. “Additionally, up to 46% of nAMD patients using anti-VEGF reagents have shown poor response or have developed tachyphylaxis with anti-VEGF therapies. HG202 is a novel CRISPR/Cas13 RNA-targeting-based gene-editing strategy suppressing the expression of VEGFA. We are particularly encouraged by the animal and human data indicating that HG202 may stabilize blood vessels and reduce fluid in the retina to potentially treat nAMD patients who are either responsive or non-responsive to anti-VEGF agents. At HuidaGene, we have made significant advancements in our efforts to treat retinal diseases. We look forward to sharing recent progress in preclinical and clinical data on our HG202 CRISPR RNA-targeting therapy program for AMD and HG004 gene replacement therapy program for LCA2 which has been granted both orphan drug and rare pediatric disease designations for inherited retinal dystrophies associated with RPE65 mutations by the U.S. FDA.”
About Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), characterized by the abnormal growth of blood vessels in the choroid under the macular of the retina, is one the leading causes of blindness globally in adults aged 50 and older if left untreated. Neovascular AMD (nAMD) or “wet” AMD (wAMD) is an advanced form of the disease that can cause rapid and severe vision loss. Nearly 50 million people over the age of 60 worldwide are living with nAMD, and the condition will affect even more people around the world as the global population ages. Current anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapies have significantly changed the landscape for the treatment of wAMD, becoming the golden standard of care. These therapies, however, have short half-lives, which necessitate life-long monthly or bimonthly repeated intraocular injections to maintain efficacy. However, persistent fluid or recurrent exudation still occurs despite standardized anti-VEGF therapy.
About RPE65 Mutation-Associated Inherited Retinal Dystrophies (RPE65-IRD)
Inherited retinal dystrophies (IRDs) are a group of rare blinding conditions caused by mutations in any 1 of more than 250 genes. Leber’s congenital amaurosis (LCA), severe early childhood-onset retinal dystrophy (SECORD), early-onset severe retinal dystrophy (EOSRD), and retinitis pigmentosa (RP), which may all be grouped under the heading of RPE65 mutation-associated inherited retinal dystrophies, are considered to represent a phenotypic continuum of the same disease. The RPE65 mutation-associated inherited retinal dystrophies with a typical onset between birth and five years of age exhibit several common clinical findings, chiefly night blindness (light staring with profound nyctalopia and nystagmus), progressive loss of visual fields, and loss of central vision. The percentage of patients (with biallelic RPE65 mutations) meeting the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for blindness increased with age and reached 100% after the age of 40 years. Given the often severe and early visual loss associated with RPE65 inherited retinal dystrophies, other areas of development, including speech, social skills, and behavior, may also be delayed.
About HG20201 Multi-Center Clinical Trial (NCT06031727)
HG20201 (SIGHT-I study) is an open-label, multicenter, dose-escalation study of a single subretinal injection of HG202, a single adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector packaging CRISPR/Cas13 RNA-targeting therapy to inhibit VEGF expression via. gene knockdown, in nAMD patients who are non-responsive or treatment-resistant to anti-VEGF therapies. The primary objectives are the safety and tolerability of HG202 at different doses. Secondary objectives include mean change in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), central retinal thickness (CRT), and the need for anti-VEGF rescue injections. After completing the primary study period, subjects will continue to be assessed in a long-term follow-up study of HG202. Two leading retinal centers (Tianjin Medical University Eye Institute and Shanghai Eye and ENT Hospital of Fudan University) in China are participating in this SIGHT-I clinical trial for HG202. For more information, please contact HG20201@huidagene.com or visit http://clinicaltrials.gov
About HG00401 First-in-Human Clinical Trial (NCT06088992)
HG00401 (LIGHT study) is an open-label, single-center, dose-escalation study of a single subretinal injection of HG004, an AAV-based gene replacement therapy, in adults and pediatrics with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophies (IRDs). In the dose escalation period, subjects were enrolled with one twenty-fifth (1/25) dose and two-thirds (2/3) of the volume compared with LUXTURNA. The objectives of the LIGHT study are to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and clinical activity such as the visual function of HG004. For more information, please contact HG00401@huidagene.com or visit http://clinicaltrials.gov
About HuidaGene
HuidaGene utilizes its proprietary HG-PRECISE® platform to discover, engineer, and develop CRISPR-based genomic medicine. The Company is advancing clinical programs of HG004 in RPE65-associated inherited retinal disease (granted ODD and RPDD), HG202 CRISPR RNA-editing in neovascular age-related macular degeneration, and the preclinical pipeline, including HG204 CRISPR RNA-editing in neurodevelopmental disease of MECP2 duplication syndrome (granted ODD and RPDD), HG302 CRISPR DNA-editing for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (granted ODD and RPDD), and HG303 CRISPR DNA-editing for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). HuidaGene’s extensive intellectual property portfolio positions it as a leader in unleashing the full potential of genome medicines for neurology and ophthalmology. Learn more at huidagene.com or on LinkedIn.
recommendations
-
Dec 12,2024
HuidaGene Therapeutics Initiates M.U.S.C.L.E. Clinical Trial of HG302 for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Completes First Patient Dosed
-
Apr 11,2025
HuidaGene at CRISPR MEDiCiNE 2025: A Celebration of Progress, Promise, and Patients
-
Nov 04,2024
HuidaGene Therapeutics Receives the First-Ever FDA Clearance of CRISPR/Cas13 RNA-Editing HG202 for Macular Degeneration
-
Dec 06,2024
HuidaGene Therapeutics Announced First Patient Dosed in the HERO Clinical Trial of HG204 for MECP2 Duplication Syndrome

