Your privacy is very important to us. When you visit our website, please agree to the use of all cookies. For more information about personal data processing, please go to Privacy Policy.


What is RPE65 Mutation-associated Inherited Retinal Diseases (RPE65-IRDs)?
Inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) are a group of rare blinding conditions caused by mutations in any one of more than 250 genes. Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis (LCA), severe early childhood-onset retinal dystrophy (SECORD), early-onset severe retinal dystrophy (EOSRD), and retinitis pigmentosa (RP), which may all be grouped under the heading of RPE65 mutation-associated IRDs, are considered to represent a phenotypic continuum of the same disease with the estimated prevalence of 2 per 100,000 people. The RPE65-IRDs have a typical onset between birth and five years of age. The percentage of patients (with biallelic RPE65 mutations) meeting the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for blindness increased with age and reached 100% after the age of 40 years. Given the often severe and early visual loss associated with RPE65-IRDs, other areas of development, including speech, social skills, and behavior, may also be delayed.
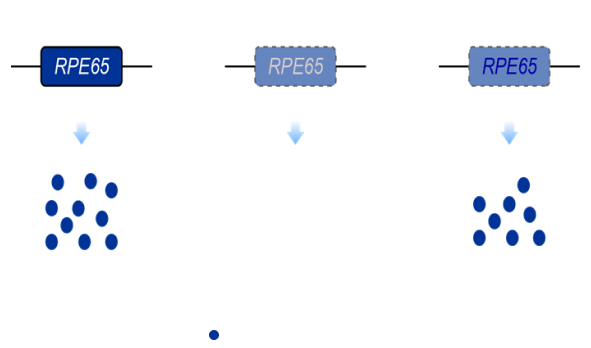
RPE65 protein converses all-trans retinyl ester to 11-cis retinol with the isomer hydrolase activity to maintain the visual cycle. Loss of RPE65 causes accumulation of retinyl esters in lipid droplets and an increase in lipofuscin granules in the RPE cells, which results in progressive retinal degeneration and loss of vision. LCA caused by the biallelic mutations of RPE65 gene is associated with severe, rod-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy, and present as night blindness in early childhood that eventually progresses to complete blindness 1, 2.
Refs:
1. Perrault I, et. al., Leber congenital amaurosis. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 1999; 68 (2): 200-208.
2. Ziccardi L, et. al., Gene therapy in retinal dystrophies.International Journal of Molecular Sciences h 2019, Nov 14; 20(22):5722.
3. Bjeloš, M., et al. RPE65 c.353G>A, p.(Arg118Lys): A Novel Point Mutation Associated with Retinitis Pigmentosa and Macular Atrophy. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23(18), 10513.
4. Gonzalez-Cordero A, et. al., Assessment of AAV vector tropisms for mouse and human pluripotent stem cell-derived RPE and photoreceptor cells.Human Gene Therapy 2018; 29(10):1124-1139.
-
27 genes are implicatedRPE65-IRD is a monogenic disease and at least

Symptoms Associated with LCA
Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is a family of congenital retinal dystrophies that results in severe vision loss at an early age. Patients present usually with nystagmus, sluggish or near-absent pupillary responses, severely decreased visual acuity, photophobia, and high hyperopia. It is the most severe retinal dystrophy causing blindness by the age of 1 year in most cases.
1) Visual
Children affected by LCA usually have very poor sight from birth. Parents will often notice that they are not responding to visual cues along with the presence of nystagmus within the first few months of life.
2) Other symptoms include
•Night blindness
•Severe light sensitivity
•Blind spots at the peripheral vision which can worsen, leading to “tunnel vision”
•Long-sightedness or rarely short-sightedness which require glasses to improve
•Deep sunken eyes as a result of the Franceschetti sign
•Strabismus (abnormal alignment of the eyes when looking at an object)
•Cataract
•Keratoconus (affects focusing of light into the retina, causing vision to be blurry and distorted)
How is LCA Diagnosed?
- LCA causes an abnormally low electrical response of the retina. An electro-diagnostic tests known as an electroretinogram (ERG) is often recommended to evaluate how the retina is working. The electrical activity of the retina is measured under different lighting conditions to determine which part of the retina is not functioning normally. This test requires the eyes to be dilated with special eye drops. A hard contact lens in each eye is also used to how the eyes respond to different kinds of light.


Treatment Options for LCA
-
Gene replacement therapy for Leber’s congenital amaurosis-The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first AAV gene therapy (LUXTURNA®; rAAV2-RPE65v2),rely on gene replacement,for inherited retinal disease (IRD) due to biallelic RPE65 gene mutations in December 2017. It’s currently the only approved to treat LCA caused by mutations to the RPE65 gene.